2/1/2019
Introduction
State legislatures have taken action to establish state licensed industrial hemp programs and promote hemp as an agricultural commodity in recent years. A wide range of products, including fibers, textiles, paper, construction and insulation materials, cosmetic products, animal feed, food, and beverages all may use hemp.
While hemp and marijuana products both are species of the cannabis plant, hemp is typically distinguished by its lower concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Federal Action
The 2018 Farm Bill changed federal policy regarding industry hemp, including the removal of hemp from the Controlled Substances Act and the consideration of hemp as an agricultural product. The bill legalized hemp under certain restrictions and expanded the definition of industrial hemp from the last 2014 Farm Bill. The bill also allows states and tribes to submit a plan and apply for primary regulatory authority over the production of hemp in their state or in their tribal territory. A state plan must include certain requirements, such as keeping track of land, testing methods, and disposal of plants or products that exceed the allowed THC concentration.
Previously, the 2014 Farm Bill defined industrial hemp and allowed for state departments of agriculture or universities to grow and produce hemp as part of research or pilot programs. Specifically, the law allowed universities and state departments of agriculture to grow or cultivate industrial hemp if:
“(1) the industrial hemp is grown or cultivated for purposes of research conducted under an agricultural pilot program or other agricultural or academic research; and
(2) the growing or cultivating of industrial hemp is allowed under the laws of the state in which such institution of higher education or state department of agriculture is located and such research occurs.”
The U.S. Department of Agriculture, in consultation with the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, released a Statement of Principles on Industrial Hemp in the Federal Register on Aug 12, 2016, on the applicable activities related to hemp in the 2014 Farm Bill.
State Action
State policymakers have taken action to address various policy issues — the definition of hemp, licensure of growers, regulation and certification of seeds, state-wide commissions and legal protection of growers. At least 41 states have enacted legislation to establish industrial hemp cultivation and production programs.
2018 Legislation Update
At least 38 states considered legislation related to industrial hemp in 2018. These bills ranged from clarifying existing laws to establishing new licensing requirements and programs. At least six states – Alaska, Arizona, Kansas, Missouri, New Jersey and Oklahoma – enacted legislation in 2018 establishing hemp research and industrial hemp pilot programs. Georgia created the House Study Committee on Industrial Hemp Production. States, already allowing for industrial hemp programs, continued to consider policies related to licensure, funding, seed certification, and other issues. For example, Tennessee amended its Commercial Feed Law to include hemp.
2017 Legislation Update
38 states and Puerto Rico considered legislation related to industrial hemp in 2017. These bills ranged from clarifying existing laws to establishing new licensing requirements and programs. At least 15 states enacted legislation in 2017 — Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Hawaii, North Dakota, Nevada, New York, Oregon, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin and Wyoming. At least four states — Florida, Nevada, New Mexico and Wisconsin — authorized new research or pilot programs.
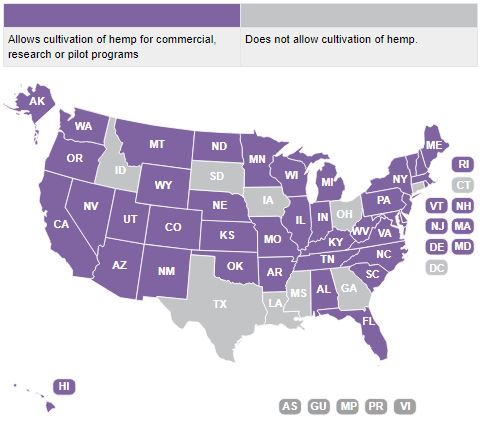
State Laws Related to Industrial Hemp
For a summary of state laws related to industrial hemp, click on the states in the map below or see the chart for a complete list of state statutes.
Defining Hemp
State statutes, with the exception of West Virginia, define industrial hemp as a variety of cannabis with a THC concentration of not more than 0.3 percent. West Virginia defines hemp as cannabis with a THC concentration of less than 1 percent.
Many state definitions for industrial hemp specify that THC concentration is on a dry weight basis and can be measured from any part of the plant. Some states also require the plant to be possessed by a licensed grower for it to be considered under the definition of industrial hemp.
Research and Pilot Programs
States have passed laws creating or allowing for the establishment of industrial hemp research or pilot programs. State agencies and institutions of higher education administer these programs in order to study the cultivation, processing, and economics of industrial hemp. Pilot programs may be limited to a certain period of time and may require periodic reporting from participants and state agencies. Some states establish specific regulatory agencies or committees, rules, and goals to oversee the research programs. States may also require coordination between specific colleges or universities and the programs, in other states coordination is optional. From 2015 to 2016, seven states enacted legislation to create hemp research or pilot programs, including Pennsylvania (H.B. 976) and Hawaii (S.B. 2659).
While industrial hemp research and pilot programs typically focus on studying the cultivation, processing for certain products and economic impacts of hemp, some states have specific guidelines and intended goals. Here are some examples of unique state research goals:
- Colorado S.B. 184 (2014) created an Industrial Hemp Grant Research Program for state universities to research and develop hemp strains that are best suited for industrial applications and develop new seed strains.
- Colorado S.B. 109 (2017) directed the commissioner of agriculture to create a group to study the feasibility of hemp products’ use in animal feed.
- Kentucky’s industrial hemp research program studies the environmental benefit or impact of hemp, the potential use of hemp as an energy source or biofuel, and the agronomy research being conducted worldwide relating to hemp.
- The North Carolina Hemp Commission studies the best practices for soil conservation and restoration in collaboration with two state universities.
Licensing, Registration and Permitting
To comply with state regulations for commercial and research programs, growers must be licensed, registered or permitted with the state agency overseeing the program. Requirements for registration, licenses and permits might include:
- Criminal background checks.
- Periodic renewals, usually every one to three years.
- Registering the location or Global Positioning System (GPS) coordinates of grow sites.
- Record keeping and reporting any sales or distributions including to whom it was sold or distributed, including processors.
- Documentation from the state agency or institution of higher education to prove the grower is participating in an approved program.
The state agencies overseeing these programs are typically authorized to conduct inspections, test the plants and review records. State agencies may revoke licenses and impose civil and criminal penalties against growers who violate regulations.
Seed Certification and Access
Access to viable seed may present a challenge for research programs and commercial growers. To implement commercial and research hemp programs, farmers need access to seeds that are guaranteed to produce plants that fall under the legal definition of hemp. These seeds can be difficult to obtain, however, because hemp is still regulated under the federal Controlled Substances Act. In response to this problem, Colorado’s governor sent a letter to the U.S. secretary of agriculture in 2014 requesting the federal government address hemp seed regulations.
States are taking independent action to regulate industrial hemp seeds. Certified seeds are usually defined as seeds that contain less than 0.3 percent THC or produce hemp plants that contain less than 0.3 percent THC.
At least four states have also established specific licenses or certification programs for hemp seed distributors and producers:
- California requires seed breeders to register with their local county agricultural commissioner.
- Indiana allows growers who obtain an agricultural hemp seed production license to produce seeds. Licensees may then sell seeds or retain them to propagate future crops.
- Maine allows the commissioner of agriculture, conservation and forestry to issue licenses to seed distributors if their seeds are from a certified seed source.
- Oregon requires growers who produce hemp seeds capable of germination to register with the Oregon Department of Agriculture if they intend to sell seeds. Growers who wish to retain seeds do not need to register as a seed producer.
| State | Citation | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Ala. Code § 2-8-380 to 2-8-383 and § 20-2-2 (2016) | Creates an industrial hemp research program overseen by the Alabama Department of Agriculture and Industries to study hemp.The department may coordinate the study with institutions of higher education. |
| Alaska | Alaska Stat. § 03.05.010; Alaska Stat. § 03.05.100; Alaska Stat. § 03.05.076 to 03.05.079; Alaska Stat. § 11.71.900; Alaska Stat. § 17.20.020; Alaska Stat. §17.38.900 (2018) | Directs the commissioner of natural resources to adopt regulations related to industrial hemp including approved sources or varieties of seed, testing requirements, and establishing isolation distances.Specifies registration requirements and allowable activities for registered producers of industrial hemp.Directs the department to establish fee levels to cover regulatory costs and annually review these fee levels.Allows for the creation of a pilot program by an institution of higher education or the Department of Natural Resources.Defines both industrial hemp and cannabidiol oil. Amends definitions for hashish oil and marijuana.Clarifies that the addition of industrial hemp to food does not create an adulterated food product.Requires a report on or before Dec. 1, 2024. |
| Arizona | SB 1098 (2018) | Authorizes a pilot program for the research, growth, cultivation and marketing of industrial hemp and establishes the Industrial Hemp Trust Fund.Directs the Arizona Department of Agriculture (AZDA) to adopt rules for the licensing, production and management of hemp and hemp seed, to set fees to fund AZDA’s activities, and to establish an industrial hemp advisory council.Allows for commercial hemp production, processing, manufacturing |
| Arkansas | Ark. Stat. Ann. § 2-15-401 et seq. (2017) | Creates the Arkansas Industrial Hemp Program including a 10-year research program. Authorizes the State Plant Board to adopt rules to administer the research program and license growers.Requires the State Plant Board to provide an annual report starting Dec. 31, 2018.Allows the University of Arkansas’s Division of Agriculture and the Arkansas Economic Development Commission to work with the State Plant Board.Establishes a separate program fund, which will include feeds collected and other sources of funding |
| California | Cal. Food and Agric. Code §81000 to 81010 (2016) | Allows for a commercial hemp program overseen by the Industrial Hemp Advisory Board within the California Department of Food and Agriculture.Establishes registration for seed breeders.This division will not become operative unless authorized under federal law. |
| Colorado | Colo. Rev. Stat. § 35-61-101 to 35-61-109 (2016) | Allows hemp cultivation for commercial and research purposes to be overseen by the Industrial Hemp Committee under the Department of Agriculture.Establishes a seed certification program.Establishes a grant program for state institutions of higher education to research new hemp seed varieties. |
| Connecticut | 2014 Conn. Acts, P.A. #14-191 (Reg. Sess.) | Created an industrial hemp feasibility study which reported to the state legislature on Jan. 1, 2015. |
| Delaware | Del. Code Ann. tit. 3 § 2800 to 2802 (2016) | Establishes an industrial hemp research program overseen by the Delaware Department of Agriculture.Allows the department to certify institutions of higher education to cultivate hemp for research purposes. |
| Florida | S 1726 (Enacted; Effective June 16, 2017) | Directs the Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services to authorize and oversee the development of industrial hemp pilot projects at certain universities. Commercialization projects may be allowed after two years with certain conditions.Authorizes the universities to develop pilot projects in partnership with public, nonprofit, and private entities;Requires a university to submit a report within two years of establishing a pilot program. |
| Hawaii | Hawaii Rev. Stat. § 141A to 141J and § 712 (2016) | Establishes an industrial hemp pilot program overseen by the Hawaii Department of Agriculture.Allows the Board of Agriculture to certify hemp seeds. |
| Illinois | Ill. Ann. Stat. ch. 720 § 550/15.2 (2016) | Creates an industrial hemp pilot program which allows the Illinois Department of Agriculture or state institutions of higher education to grow hemp for research purposes.Requires institutions of higher education provide annual reports to the department. |
| Indiana | Ind. Code Ann. § 15-15-13-1 to 15-15-13-17 (2016) | Allows the production and possession of hemp by licensed growers for commercial and research purposes.Growers and handlers of hemp seeds must obtain a hemp seed production license.Nothing in this section allows anyone to violate federal law. |
| Kansas | K.S.A Ch. 62 § 1 – 62 § 2 SB 263 (2018) | Creates the Alternative Crop Research Act (and licensing fee fund) to promote the research and development of industrial hemp.Allows the Kansas Department of Agriculture (KDA), either alone or in coordination with a state institute of higher education, to cultivate and promote research and development of industrial hemp.Directs KDA to oversee annual licensing, establish fees, and promulgate rules and regulations.Allows for a pilot program in Russell County, and other counties as determined by KDA. |
| Kentucky | Ky. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 260.850 to 260.869 (2016) | Creates an industrial hemp research program and a commercial licensing program to allow hemp cultivation for any legal purpose.The commercial growers’ license shall only be allowed subject to the legalization of hemp under federal law.Growers are required to use certified seeds and may import or resell certified seeds.Mandates the University of Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station oversee a five-year hemp research program.Creates the Industrial Hemp Commission, attached to the Agricultural Experiment Station, to oversee, among other things, the licensing, testing and implementation of regulations and rules related to hemp. |
| Maine | Me. Rev. Stat. Ann. tit. 7 § 2231 (2016) | Allows hemp growing for commercial purposes.Establishes a license for seed distributors. |
| Maryland | Md. Agriculture Code Ann. § 14-101 (2016) | Establishes a license allowing individuals to plant, grow, harvest, possess, process, sell, or buy industrial hemp in Maryland.Authorizes the Maryland Department of Agriculture or an institution of higher education to grow hemp for research purposes. |
| Massachusetts | Mass. Gen. Laws. Ann. 128 § 116 to 123 (2017) | Allows for hemp to be planted, grown, harvested, possessed, bought or sold for research or commercial purposes under the regulation of the Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources (MDAR).Requires producers and distributors to obtain a license issued by MDAR and for persons utilizing hemp for commercial or research purposes to register with MDAR.Directs MDAR and Commissioner of Agriculture to promulgate rules and regulations. |
| Michigan | Mich. Comp. Laws § 286.841 to 286.844 (2016) | Creates an industrial hemp research program allowing the Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development and institutions of higher education to grow hemp for research purposes. |
| Minnesota | Minn. Stat. § 18K.01 to 18K.09 (2016) | Establishes a commercial hemp licensing program overseen by the Minnesota commissioner of agriculture.Applicants must prove they comply with all federal hemp regulations, meaning that commercial licenses may not be available until federal law changes.Allows the commissioner to implement an industrial hemp pilot program. Institutions of higher education may apply to participate in this program. |
| Missouri | HB 2034 (2018) | Creates an industrial hemp agricultural pilot program, in accordance with federal law, to be implemented by the Missouri Department of Agriculture (MDA) to study the growth, cultivation, processing, feeding and marketing.Creates the Industrial Hemp Fund.Directs MDA to promulgate rules, such as establishing permit and registration fees, to implement the program.Allows the Missouri Crop Improvement Association to establish and administer a seed certification program; specifies the food containing industrial hemp may not be considered adulterated. |
| Montana | Mont. Code Ann. § 80-18-101 to 80-18-111 (2016) | Allows the Montana Department of Agriculture to implement a commercial hemp licensing program.Requires commercial growers to use certified seeds.Requires a federal controlled substances registration from the DEA for the affirmative defense against marijuana charges to apply. |
| Nebraska | Neb. Rev. Stat. § 2-5701 (2016) | Allows a postsecondary institution or the Nebraska Department of Agriculture to grow hemp for research purposes. |
| Nevada | Nev. Rev. Stat. § 557.010 to 557.080 (2016) | Mandates the Nevada Board of Agriculture implement an industrial hemp pilot program.Allows institutions of higher education and the Nevada Department of Agriculture to grow hemp for research purposes. |
| New Hampshire | N.H. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 433-C:1 to 433-C:3 (2016) | Allows institutions of higher education to cultivate hemp for research purposes.All research must be coordinated with the New Hampshire Department of Agriculture, Markets and Food.All research projects must conclude within three years of commencement. |
| New Hampshire | 2014 N.H. Laws, Chap. 18 | Established a committee to study the growth and sale of industrial hemp in New Hampshire.The study was required to report their findings by Nov. 1, 2014. |
| New Jersey | AB 1330 / SB 3145 (2018) | Directs the New Jersey Department of Agriculture to create a pilot program to research industrial hemp cultivation.Exempts anyone participating in the agricultural pilot program from crimes and penalties relating to the purchase, sale, or cultivation of marijuana. |
| New Mexico | SB 6 (2017) | Directs the New Mexico Department of Agriculture to adopt rules for the research and development of industrial hemp, including for licensure, law enforcement training, inspection, recordkeeping, fees and compliance processes.Establishes the New Mexico Industrial Hemp Research and Development Fund. |
| New York | N.Y. Agriculture and Markets Law § 505 to 508 (McKinney 2016) | Allows the growth of hemp as part of an agricultural pilot program by the Department of Agriculture and Markets and/or an institution of higher education.The commissioner of agriculture and markets may authorize no more than 10 sites for growing hemp as part of a pilot program.The commissioner may develop regulations to authorize the acquisition and possession of industrial hemp seeds.1 NYCRR 159.2 allows authorized growers to possess, grow and cultivate seeds and hemp plants. |
| North Carolina | N.C. Gen. Stat. § 106-568.50 to 106-568.54 and § 90-87(16) (2016) | Creates an agricultural hemp pilot program overseen by the North Carolina Industrial Hemp Commission within the North Carolina Department of Agriculture.The commission must collaborate with North Carolina State University and North Carolina A&T State University. |
| North Dakota | N.D. Cent. Code § 4-41-01 to 4-41-03 and § 4-05.1-05 (2016) | Allows hemp cultivation for commercial or research purposes overseen by the North Dakota agricultural commissioner.Growers must use certified seeds. Licensees may import, resell and plant hemp seeds.Permits the North Dakota State University-Main Research Center to conduct research on industrial hemp and hemp seeds. |
| Oklahoma | OK ST T. 2 § 3-401 HB 2913 (2018) | Creates the Oklahoma Industrial Hemp Agriculture Pilot Program and revolving fund for the program.Allows universities, or subcontractors, to cultivate industrial hemp for research and development purposes.Directs the Oklahoma Department of Agriculture, Food, and Forestry to manage the pilot program, establish a certified seed program, and promulgate rules related to licensing, inspections. |
| Oregon | Or. Rev. Stat § 571.300 to § 571.315 (2016) | Allows individuals registered by the Oregon Department of Agriculture to grow hemp for commercial purposes.Growers and handlers who intend to sell or distribute seeds must be licensed as seed producers. |
| Pennsylvania | Pa. Cons. Stat. Ann. tit. 3 § 701 to 710 (Purdon 2016) | Allows institutions of higher education or the Department of Agriculture of the commonwealth to research hemp under an industrial hemp pilot program.This chapter shall expire if the secretary of agriculture of the Commonwealth determines a federal agency is authorized to regulate hemp. |
| Rhode Island | R.I. Gen. Laws § 2-26-1 to 2-26-9 (2016) | Establishes a commercial hemp program overseen by the Department of Business Regulation.Allows the Division of Agriculture in the Department of Environmental Management to assist the Department of Business Regulation in regulating hemp.Growers must verify they are using certified seeds.The department shall authorize institutions of higher education to grow hemp for research purposes. |
| South Carolina | S.C. Code Ann. § 46-55-10 to 46-55-40 (Law. Co-op 2016) | Allows hemp growth for commercial and research purposes. |
| Tennessee | Tenn. Code Ann. § 43-26-101 to 43-26-103 (2016) | Allows commercial hemp production overseen by the Tennessee Department of Agriculture.Directs the commissioner of agriculture to develop licensing rules for processors and distributors.Allows institutions of higher education to acquire and study seeds for research and possible certification. |
| Utah | Utah Code Ann. § 4-41-101 to 4-41-103 (2016) | Allows the Utah Department of Agriculture to grow hemp for research purposes.Requires that the department certify institutions of higher education to grow hemp for research purposes. |
| Vermont | Vt. Stat Ann. tit. 6 § 561 to 566 (2016) | Allows for commercial hemp production overseen by the Vermont secretary of agriculture, food and markets.Requires the registration form advise applicants that hemp is still listed and regulated as cannabis under the federal Controlled Substances Act. |
| Virginia | Va. Code § 3.2-4112 to 3.2-4120 (2016) | Authorizes research and commercial hemp programs overseen by the Virginia Board of Agriculture and Consumer Services and the Virginia commissioner of agriculture and human services.The commissioner must establish separate licenses for the research program and for commercial growers.Nothing in this chapter allows individuals to violate federal laws. |
| Washington | Wash. Rev. Code Ann. § 15.120.005 to 15.120.050 (2016) | Allows hemp production as part of a research program overseen by the Washington State Department of Agriculture.Requires the department establish a seed certification program. |
| West Virginia | W. Va. Code. § 19-12E-1 to 19-12E-9 (2016) | Allows hemp production for commercial purposes by growers licensed by the West Virginia Commissioner of Agriculture.Growers must use seeds which produce plants containing less than 1 percent THC. |
| Wisconsin | Wis. Stat. §94.55; Wis. Stat. §94.67; Wis. Stat. §97.02; §348.27; Wis. Stat. §961.14; Wis. Stat. §961.32; Wis. Stat. §961.442; Wis. Stat. §961.55; Wis. Stat. §973.01 (effective Dec. 2, 2017) (Also, see 2017 Act 100 or S.B. 119.) | Directs the state Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP) to establish a state industrial hemp program.Includes GPS coordinates, fee payment and a criminal history search as requirements for licenses.Directs the DATCP to establish and administer a seed certification program or designate another agency or organization to administer the program.Requires the DATCP to create a pilot program to study the growth, cultivation and marketing of industrial hemp.Specifies exemptions from prosecution under the state Uniform Controlled Substances Act.Amends the definition of agricultural commodity to include industrial hemp. |
| Wyoming | Wyo. Stat. § 35-7-2101 to 35-7-2107 (effective July 1, 2017) | Authorizes the planting, growing, harvesting, possession, processing, or sale of industrial hemp for licensed individuals.Provides for licensing requirements and rule-making authority by the state department of agriculture.Allows the University of Wyoming and the state department of agriculture to grow industrial hemp for research purposes.Provides an affirmative defense for marijuana possession or cultivation of marijuana for licensed industrial hemp growers. |
PLEASE NOTE: NCSL cannot provide advice or assistance to private citizens or businesses regarding industrial hemp laws or other related matters. Please consult your state department of agriculture or a private attorney.
Source:
http://www.ncsl.org/research/agriculture-and-rural-development/state-industrial-hemp-statutes.aspx














